A few weeks ago, we talked about my favorite Mediterranean pantry staple, and the one ingredient I reach for daily: extra virgin olive oil (EVOO for short). One of the biggest questions people ask is whether they can cook with olive oil. Let’s dive a bit deeper into some common concerns specifically around cooking with olive oil, as well as reasons why extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) is both safe to cook with and my cooking oil of choice.
Can you cook with olive oil?
The short answer is yes, you can cook with olive oil! In fact, it is the main cooking fat in my Mediterranean cooking. I use extra virgin olive oil for pretty much everything from making the perfect Greek salad dressing and basil pesto, to a light pasta sauce, or a marinade for my grilled chicken and beef kebabs, or to roast vegetables, and more! EVOO is the start of every delicious pot of stew or perfectly charred roasted vegetables I’ve made. And yes, I even bake with it! More on the baking thing later. I’ve heard false rumors stating that olive oil is not safe to cook because of its low smoke point or because heating it causes the oil harmful compounds and more trans fats forming. These are myths that research has busted time and time again. While the smoke point of olive oil is lower than other cooking oils, it is actually able to remain stable at high heat, and that’s the important thing to focus on (more on this later).
Smoke point
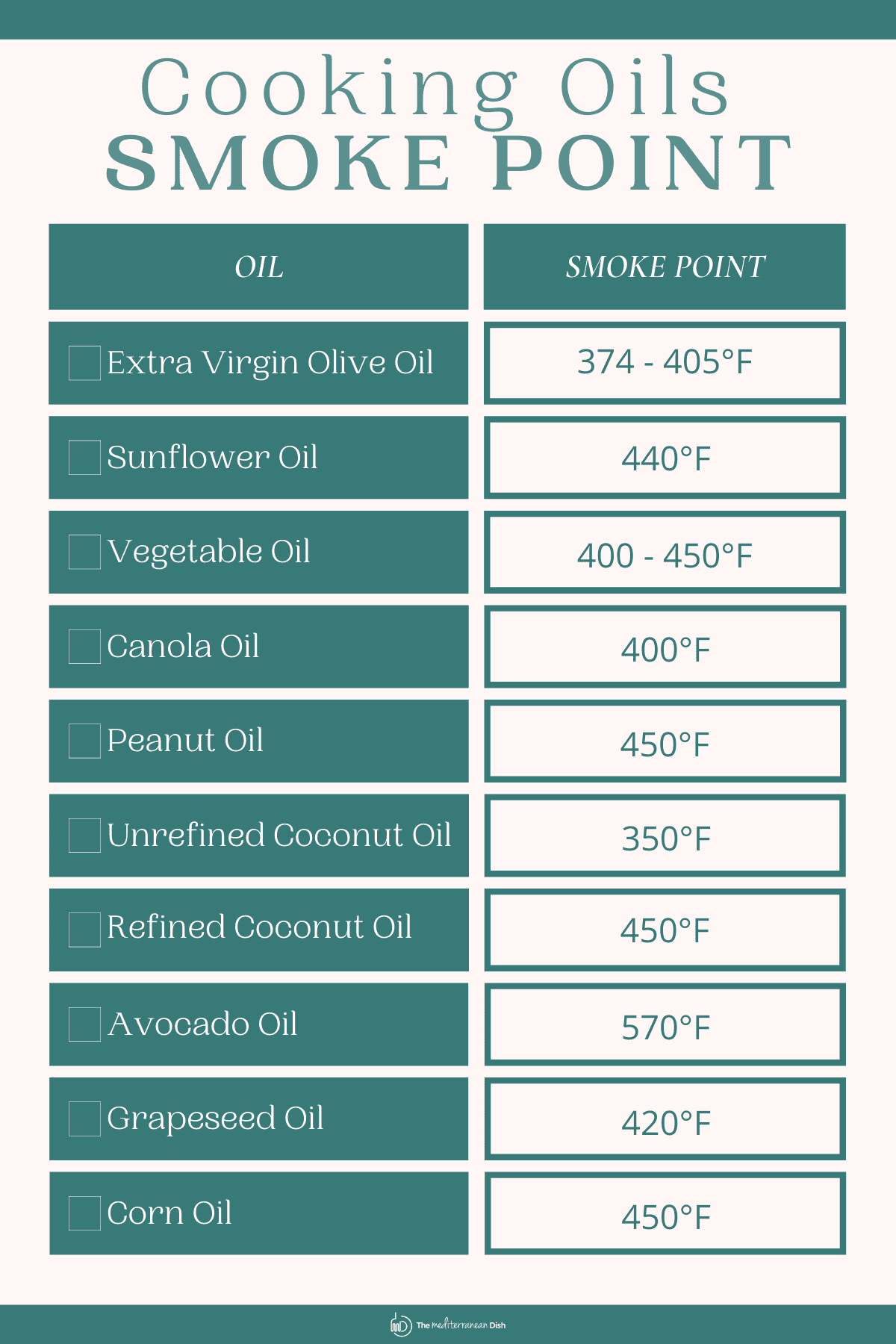
One of the main concerns surrounding the question, “Can you cook with olive oil” is its smoke point. The smoke point of an oil is the temperature at which it starts to smoke. In the case of olive oil, that is between 374 and 405 degrees F (190 to 207 degrees C). Here’s how it compares to the smoke point of common cooking oils:
Sunflower oil – 440 degrees F Vegetable oil – 400 to 450 degrees F Canola oil – 400 degrees F Peanut oil – 450 degrees F Unrefined coconut oil – 350 degrees F Refined coconut oil – 450 degrees F Avocado oil – 570 degrees F Grapeseed oil – 420 degrees F Corn oil – 450 degrees F
But when cooking with oil, it is the oxidative stability that one should focus more on. Olive oil is more stable to cook with than many other oils.
Oxidative stability
According to the North American Olive Oil Association, the smoke point of a cooking oil should not be the top concern, but rather the oxidative stability levels. Oxidative stability has to do with how resistant the oil fats are to reacting when exposed to oxygen, heat, and light. Even though olive oil has a lower smoke point than other cooking oils, quality extra virgin olive oil is still a good option option for cooking. The main thing that happens when olive oil is heated is that some of the flavor compounds will evaporate. This means that some of the rich, pungent flavor is lost in the cooking process, however, in most cases, the oil remains stable and retains most of its beneficial nutrients. This is because of EVOO’s antioxidant properties and its fat composition. I’m about to get into some food science here, but bear with me. Extra virgin olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats (MUFAs), which are quite heat stable and a bit less likely to undergo oxidization (unless under extreme conditions, perhaps). Some examples of monounsaturated fats are oleic acid, palmitic acid, and linoleic acid. MUFAs are also considered to be healthy fats, and are anti-inflammatory, heart healthy, and may help with weight loss. The type of fat that we should be concerned about are polyunsaturated fats (PUFAs), which are unstable under high heat. A 2018 study exposed a range of oils to different levels of heat to determine their rate of degeneration. They found that oils higher in PUFAs (such as corn oil) produced twice the amount of harmful compounds of extra virgin olive oil – despite corn oil having a much higher smoke point than EVOO. Antioxidant levels also play a role in oxidative stability. Put simply, antioxidants help protect against oxidation — so the more antioxidants an oil has, the better. Extra virgin olive oil and virgin olive oil have high levels of antioxidants because they are not refined, which means they are better equipped to protect against oxidation. Vegetable oils and other refined oils have very low antioxidant levels, and therefore have lower oxidative stability.
Does EVOO lose its health benefits when cooked?
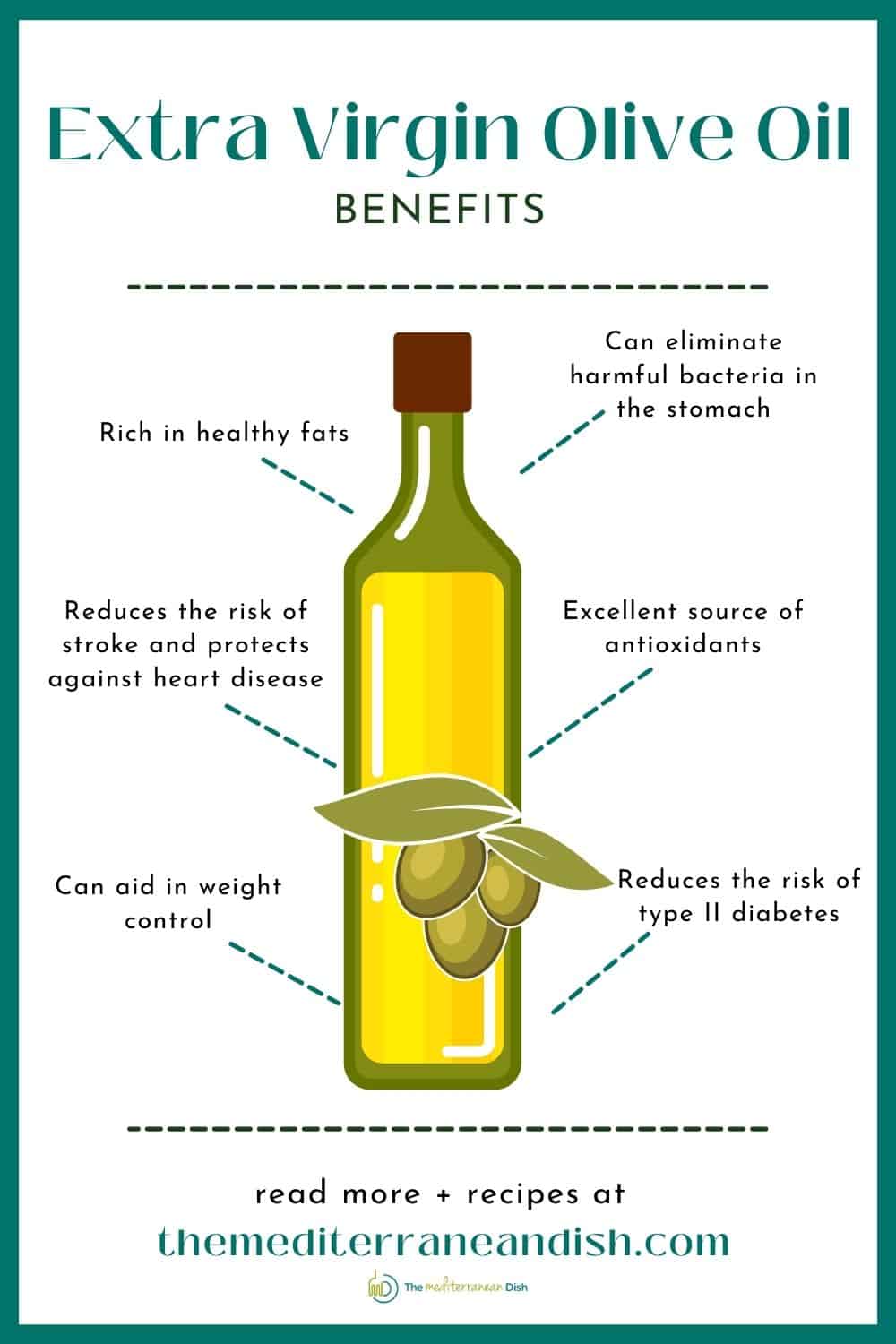
Extra virgin olive oil has long been prized for its long list of health benefits including being rich in healthy fats and antioxidants, helping to protect against heart disease and type 2 diabetes, aiding in eliminating harmful bacteria, and more. While heating extra virgin olive oil will reduce its nutrient composition, a study by the University of Barcelona published in the journal Antioxidants found that olive oil still retains large amounts of its healthy compounds. The study found that heat reduced the amount of polyphenols in olive oil, but antioxidant and polyphenol numbers remained quite high when heated. In other words, you will lose some of the nutrients when you heat the oil, but a lot of them will remain.
Types of olive oil
Enter any supermarket and you’ll likely see an enormous selection of olive oils. Choosing the best olive oil for cooking can quickly become confusing. So let’s break it down. There are four main types of olive oil:
Extra virgin olive oil – The least processed, most flavorful form of olive oil. Virgin olive oil – Not widely available, virgin olive oil is similar to EVOO, but is slightly lower quality. Pure olive oil (also known simply as “olive oil”) – The term “pure” simply means that the bottle only contains olive oil, but it is a mix of refined oil (the majority) and virgin olive oil. Pure olive oil does not have the rich taste that EVOO is known for. Light olive oil – Don’t mistake “light” to mean this type of olive oil is lower in calories. All types of olive oil have around 14 grams of fat per tablespoon. Light actually refers to the very neutral taste that light olive oil has.
Where to find the best olive oil for cooking?
Extra virgin olive oil is my favorite oil for cooking. It has the most antioxidants and nutrients and the best, richest flavor. I, like many people, find that the taste of EVOO is not overwhelming; rather, it complements and enhances the other flavors in a dish. You can find the olive oils I use daily in my cooking here via our online shop. We currently carry delicious, rich, flavorful olive oils from Greece, Spain, and Italy. For a deep dive into to tasting olive oil, check out our guide How To Taste Olive Oil: A Step-By-Step Guide To Go From The Basics To The Pros. Here are the basics:
If you like a fruity olive oil with medium intensity, try our Italian Nocellara EVOO. To many who are not big users or olive oil, this is a good one to try because it is mild and not too peppery, it is also delicious with aromas of freshly-picked tomatoes and vegetables. If you like a moderately intense olive oil with a slight bitterness and a bit of peppery finish, our Spanish Hojiblanca EVOO and our Private Reserve Greek EVOO are good options, and I use them regularly in most of my cooking. Our Early Harvest Greek EVOO is likely the most intense of the olive oils we carry, it is a prized oil from early picked olives and has a bold finish. You can certainly use it when cooking, but I do especially love it on salads, as a dip, or in my olive oil pasta where the sauce is just warmed.
Some tips to keep in mind when cooking with olive oil
There are a couple of things I recommend when cooking with olive oil. Firstly, for best flavor, as much as possible, watch when heating your olive oil. I often say to heat the oil until shimmering, but not smoking. This means you may see the oil begin to move and a slight sheen will show on the surface while some tiny bubbles form beneath. You might even see some steam. At this point, your oil is hot enough to cook with and does not need to be heated further. Secondly, use a splatter guard or splatter screen is a must-have! If you’re working with ingredients that have some water on them, the oil may begin to splatter. To avoid oil stains on your clothes and to keep safe, invest in a splatter guard. They come in different sizes to suit your skillets, and are a great way to safely cook with olive oil.
Can you bake with olive oil?
Yes, you can bake with olive oil! I use it to bake my Italian Apple Olive Oil Cake and Banana Walnut Bread, and even butter lovers agree that olive oil makes the most tender, moist baked goods. This is because EVOO is liquid at room temperature, so it creates cakes and baked goods that don’t dry out even when you have leftovers for a couple of days. Don’t worry quality, good-tasting extra virgin olive oil won’t overpower the flavors in your cakes, cookies, muffins, etc. It actually adds nuance to the flavor. And yes, not to keep harping on this point, but replacing your butter with extra virgin olive oil in your cakes is a good way to reduce your intake of saturated fat.
When to use a different oil instead
There is really only one instance when I would recommend using another oil instead of extra virgin olive oil: deep-frying. I rarely deep-fry food , but when I do,I reach for a cheaper, neutral-tasting oil, like grapeseed oil, for example. One of the main reasons why is that quality extra virgin olive oil is relatively pricey. You need a lot of oil when deep-frying, and it seems like a waste to use so much oil only to have to discard it after use. In addition, if your deep frying takes a longer period of time, olive oil would lose its flavor and start to degrade (high heat + time accelerate oxidative reactions).
Related articles you may like
Please Note: The information shared here on The Mediterranean Dish is intended for your general knowledge. It is not intended as a medical diagnosis or advice. Please be sure to consult your healthcare provider before trying a new diet or a way of eating. Never disregard professional advice or delay seeking treatment based on what you read. You are responsible for cooking properly for your own safety.
Olive Oil 101: Everything You Need to Know
What is the Mediterranean Diet and How to Follow It
What is Za’atar and How to Use It (BEST Za’atar Recipes)
35+ Bold and Easy Fish Recipes Anyone Can Make